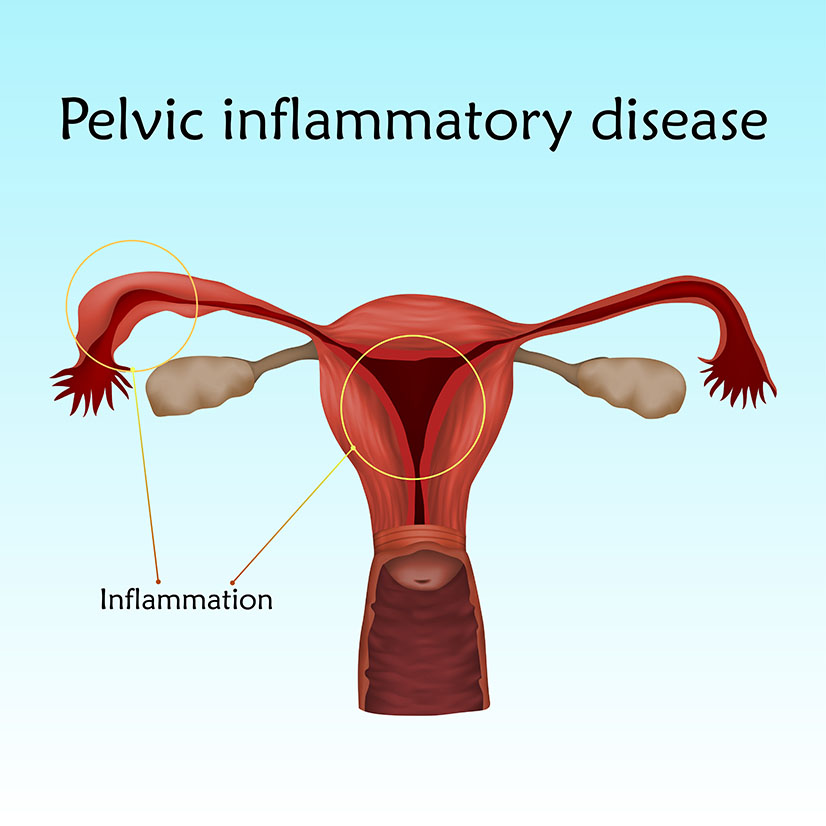
The term pelvic inflammatory disease, abbreviated as PID, is used to describe all kinds of inflammations or infections that occur along the female genital tract such as the fallopian tubes, the ovaries, cervix, uterus and pelvic tissues. The inflammation and swelling usually cause the uterus and other reproductive organs to be scarred, which often results to infertility. Eschenbach (1997) notes that in America, at least a million women are diagnosed with the pelvic inflammatory condition annually. Shan& Li (2003) say that the majority of PID sufferers fall in the reproductive age of between 15 and 40 years and have problems conceiving and delivering a healthy baby.
The term pelvic inflammatory disease, abbreviated as PID, is used to describe all kinds of inflammations or infections that occur along the female genital tract such as the fallopian tubes, the ovaries, cervix, uterus and pelvic tissues. The inflammation and swelling usually cause the uterus and other reproductive organs to be scarred, which often results to infertility. Eschenbach (1997) notes that in America, at least a million women are diagnosed with the pelvic inflammatory condition annually. Shan& Li (2003) say that the majority of PID sufferers fall in the reproductive age of between 15 and 40 years and have problems conceiving and delivering a healthy baby.
Causes of pelvic inflammation disease
The commonest causes of PID include bacteria that also cause sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. These bacteria, like STIs, are transferred from one person to another through unprotected sex with someone who is already infected. According to research, women who flush their vagina with water or some other liquid (douching) have a greater risk of getting PID than the ones who shun douching. There’s evidence showing that douching can alter properties of the components inside the vagina and this can cause unprecedented bacterial growth. Some women have contracted PID after undergoing surgery that involves the female reproductive organs and others after having intrauterine devices (IUD) inserted.
Common symptoms of pelvic inflammation disease
Some common symptoms of pelvic inflammation disease include undying pain at the pelvic area or lower abdomen, pain when urinating, vaginal discharge, chills, irregular menstruation and painful period cramps, fever, nausea and vomiting. Some patients with chronic PID may not show any signs while others have intermittent symptoms.
How pelvic inflammation disease contributes to infertility in women
PID is a general term for inflammations that normally result from infections affecting the female reproductive organs. When the inflammation occurs in the uterus, it’s termed as endometritis. This condition scars the uterus, thereby causing infertility and disrupting implantation which results to ectopic pregnancy. Salpingitis refers to a pelvic inflammation disease that affects the fallopian tubes. It causes fertility problems in that the tubes are blocked as a result of the inflammation and cannot convey the sperm or the egg. Also, the loss of libido and constant abdominal pain contributes to infertility by limiting the frequency of sexual intercourse.
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease usually results from severe infection by bacteria like streptococcal, gonorrheal and/or chlamydial. It is usually symptomized by fever, vaginal discharge, and pain at the abdomen and the lower back. This acute condition can quickly cause lasting damage to the reproductive organs and thus effective treatment is needed swiftly in order to preserve fertility.
Chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
When incorrect or ineffective treatment is administered for acute PID or it is left untreated, the disease can turn into a long term or chronic condition that doesn’t respond to the common Western medical treatments of antibiotics. Chronic PID is at times asymptomatic or it may manifest in mild erratic symptoms like exhaustion, lower back pain and abdominal pain.
Western Medical Treatments for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Western medical practitioners address acute pelvic inflammatory disease through a regimen of antibiotics that focus on eliminating a host of pathogens suspected to cause the symptoms. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published the 2015 STD Treatment Guidelines to help combat PID and other STDs. The most common antibiotics for treating PID include doxycycline, ofloxacin, ceftriaxone and metronidazole. It is important to note that symptoms may die away without the patient being healed. Even after taking the prescribed medication, some patients still exhibit PID causative pathogens.
When symptoms persist for more than six months, the condition is regarded as chronic, which Western medicine fails to offer relief for. This has necessitated sufferers and practitioners alike to turn to Oriental medicine for alternative and effective treatment for PID in the name of acupuncture. Luckily, consistent research results show that acupuncture effectively resolves pelvic inflammatory disease and remarkably enhances the capability to carry and give birth to a child in fine fettle.
Acupuncture: Effective alternative treatment for pelvic inflammatory disease
From a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) standpoint, PID is caused by damp heat, which is akin to infection in Western medicine. Acute PID transforms into a chronic condition when the damp heat is not properly treated quickly and when life’s vital energy (Qi) is obstructed and stagnates such that there’s no free flow. In simple terms, acupuncturists and Oriental medicine practitioners in general believe that PID and other conditions that inhibit a woman’s fertility emanate from compromised pelvic organs that result from blocked or imbalanced flow of Qi and blood. When Qi, blood and other body fluids fail to flow as freely as they should, the body’s immune system is greatly hampered and thus left susceptible to illnesses.
Acupuncture for PID is focused on increasing the capacity of the immune system in fighting infections and inflammations along the reproductive tract as well as eliminate pain. Acupuncture effectively helps guard the reproductive organs such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the uterus against damage. Consequently, the numerous PID patients with fertility problems or that have had ectopic pregnancies greatly benefit from acupuncture as it boosts their chances of getting pregnant and delivering a bouncing baby.
A research published by Chongqing Medical Journal concluded that acupuncture has an effective rate of 92% in treating pelvic inflammation disease. Another study conducted by Liang and Gong showed that women with PID and fertility issues were able to conceive and deliver healthily after undergoing acupuncture. The Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine also published another study that established that acupuncture has 88% success rate in eliminating PID symptoms and curing the condition. This success rate was much higher than that of the control group that was given antibiotics.
If you are suffering with Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and are looking for an effective alternative approach you have come to the right place. The Acupuncturists have the experience and skill to help. Give us a call to schedule a free consultation with one of our licensed acupuncture physicians. We proudly serve the communities of Margate, Coconut Creek, Coral Springs, Tamarac, Parkland, Deerfield Beach, and West Boca.
References
- Eschenbach, D. A. (1997). Epidemiology of pelvic inflammatory disease. In Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (pp. 1-20). Springer New York.
- Grodstein, F., & Rothman, K. J. (1994). Epidemiology of pelvic inflammatory disease. Epidemiology, 5(2), 234-242.
- Shan, H. U., & Li, L. I. (2003). Clinical observation of treatment of combination of western and traditional chinese medicines in 120 patients with chronic pelvic inflammatory disease [J]. Chongqing Medical Journal, 12, 056.
- Liang, Y., & Gong, D. (2014). Acupuncture for chronic pelvic inflammatory disease: a qualitative study of patients’ insistence on treatment. BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 14(1), 345.
- Lao, L., Huang, Y., Feng, C., Berman, B. M., & Tan, M. T. (2012). Evaluating traditional Chinese medicine using modern clinical trial design and statistical methodology: application to a randomized controlled acupuncture trial. Statistics in medicine, 31(7), 619-627.
- Alraek, T., & Malterud, K. (2009). Acupuncture for menopausal hot flashes: a qualitative study about patient experiences. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 15(2), 153-158.
- Workowski, K. A., & Bolan, G. A. (2015). Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines (2015). Reproductive Endocrinology, (24), 51-56.